Implementing Regional Failover with AWS Global Accelerator
This is a personal project. Full implementation available on GitHub
CloudSleuth requires its web application to remain accessible during regional failures or disasters. The challenge is to deliver a consistent user experience without manual server management, even when the primary region is unavailable. This architecture is designed to be scalable, reliable, and secure using AWS Global Accelerator, Route 53, CloudWatch, SSM, and Lambda. The entire infrastructure is automatically provisioned with Terraform.
Table of Contents
Implementation Strategy
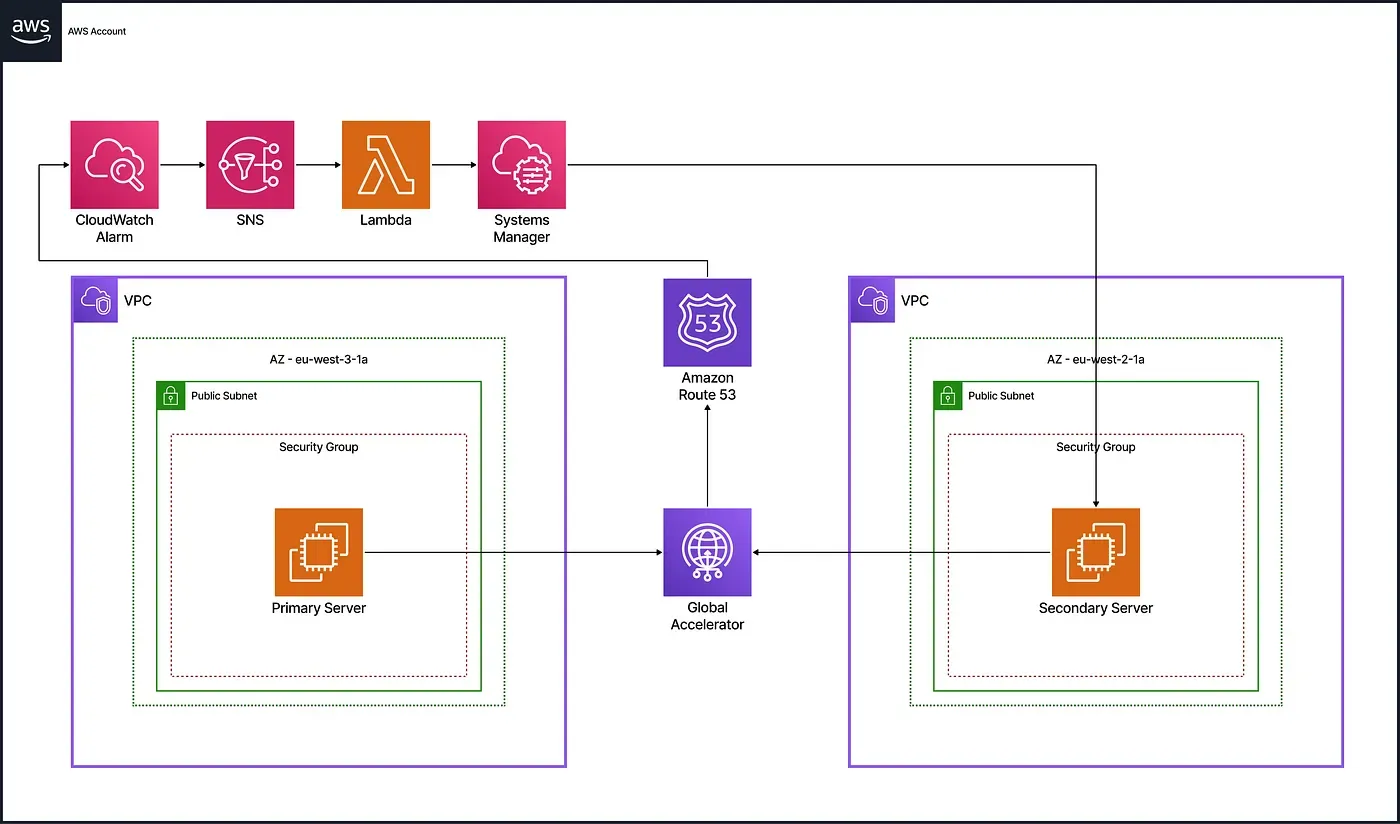
To ensure high availability and maintain access during regional outages, the architecture uses a multi-region, highly available web architecture managed entirely with Terraform. The solution uses AWS Global Accelerator to provide static IP addresses that remain consistent even during failover events. Route 53 continuously monitors the health of the primary server through HTTP checks, while CloudWatch triggers alarms when failures occur and routes notifications via SNS. Lambda functions automate the failover process by starting backup instances through Systems Manager (SSM) and updating Global Accelerator routing to redirect traffic to the secondary region. When the primary server recovers, routing is restored to the original region without user impact.
Technical Implementation
Multi-Region Infrastructure
The infrastructure includes two VPCs in Paris and London, each with a public subnet and EC2 instance. The primary server runs by default in Paris, while the secondary in London stays in pilot light mode and starts only during failover.
VPC Module
resource "aws_vpc" "main" {
cidr_block = "10.0.0.0/16"
enable_dns_support = true
enable_dns_hostnames = true
}
resource "aws_subnet" "public" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.main.id
cidr_block = "10.0.1.0/24"
map_public_ip_on_launch = true
}
resource "aws_security_group" "web_sg" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.main.id
ingress {
from_port = 80
to_port = 80
protocol = "tcp"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
}EC2 Module
data "aws_ami" "amazon_linux" {
most_recent = true
owners = ["137112412989"]
filter {
name = "name"
values = ["al2023-ami-*-x86_64"]
}
}
resource "aws_instance" "web" {
ami = data.aws_ami.amazon_linux.id
instance_type = "t2.micro"
subnet_id = var.subnet_id
vpc_security_group_ids = [var.security_groups]
user_data = <<-EOF
#!/bin/bash
yum install -y httpd
systemctl start httpd
echo "Hello from ${var.server_message}" > /var/www/html/index.html
%{ if !var.start_on_boot }
shutdown -h now
%{ endif }
EOF
}Regional Module Usage
module "primary_vpc" {
source = "./modules/infra/vpc"
providers = {
aws = aws.paris
}
}
module "primary_webserver" {
providers = {
aws = aws.paris
}
source = "./modules/infra/ec2"
security_groups = module.primary_vpc.security_groups_id
subnet_id = module.primary_vpc.subnet_id
server_message = "primary webserver"
start_on_boot = true
}
# For the secondary region (London), we use the same modules
# with the aws.london provider and start_on_boot = falseGlobal Accelerator Configuration
AWS Global Accelerator offers two static IP addresses for consistent access during failover. It uses a TCP listener on port 80 with two endpoint groups: the primary region handles all traffic by default, while the secondary stays on standby.
resource "aws_globalaccelerator_accelerator" "global_accelerator" {
name = "Website"
ip_address_type = "IPV4"
enabled = true
}
resource "aws_globalaccelerator_listener" "http_listener" {
accelerator_arn = aws_globalaccelerator_accelerator.global_accelerator.id
protocol = "TCP"
port_range {
from_port = 80
to_port = 80
}
}
resource "aws_globalaccelerator_endpoint_group" "primary_endpoint" {
listener_arn = aws_globalaccelerator_listener.http_listener.arn
endpoint_group_region = "eu-west-3"
endpoint_configuration {
endpoint_id = module.primary_webserver.ec2_id
weight = 100
client_ip_preservation_enabled = true
}
depends_on = [module.primary_webserver]
}
resource "aws_globalaccelerator_endpoint_group" "secondary_endpoint" {
listener_arn = aws_globalaccelerator_listener.http_listener.arn
endpoint_group_region = "eu-west-2"
endpoint_configuration {
endpoint_id = module.secondary_webserver.ec2_id
weight = 0
client_ip_preservation_enabled = true
}
depends_on = [module.secondary_webserver]
}Monitoring & Alerts
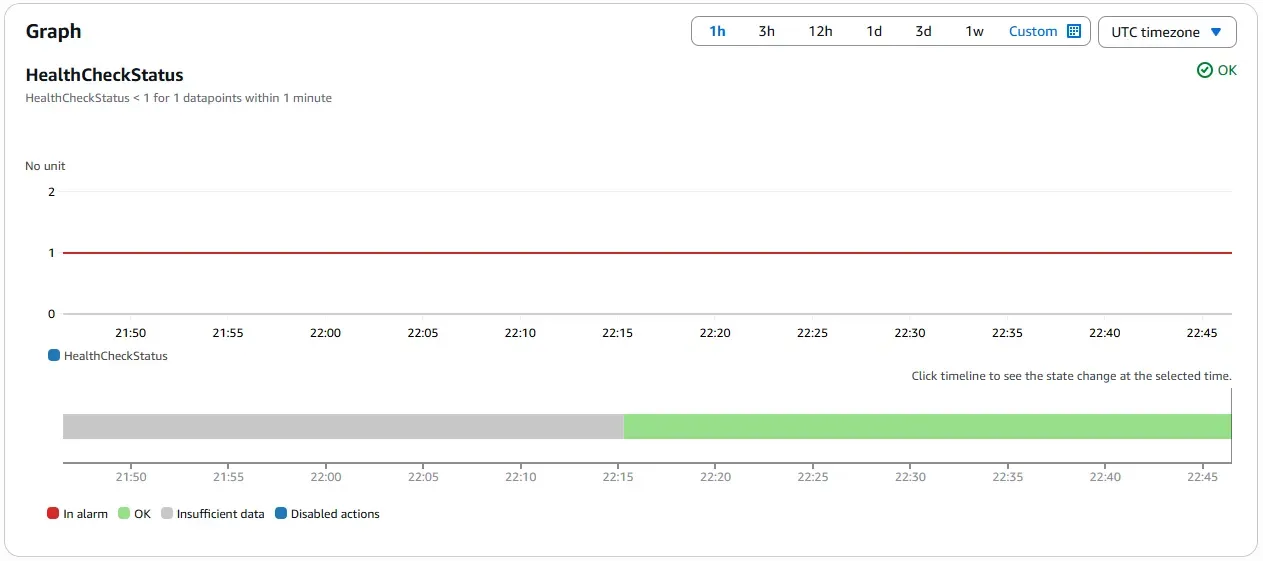
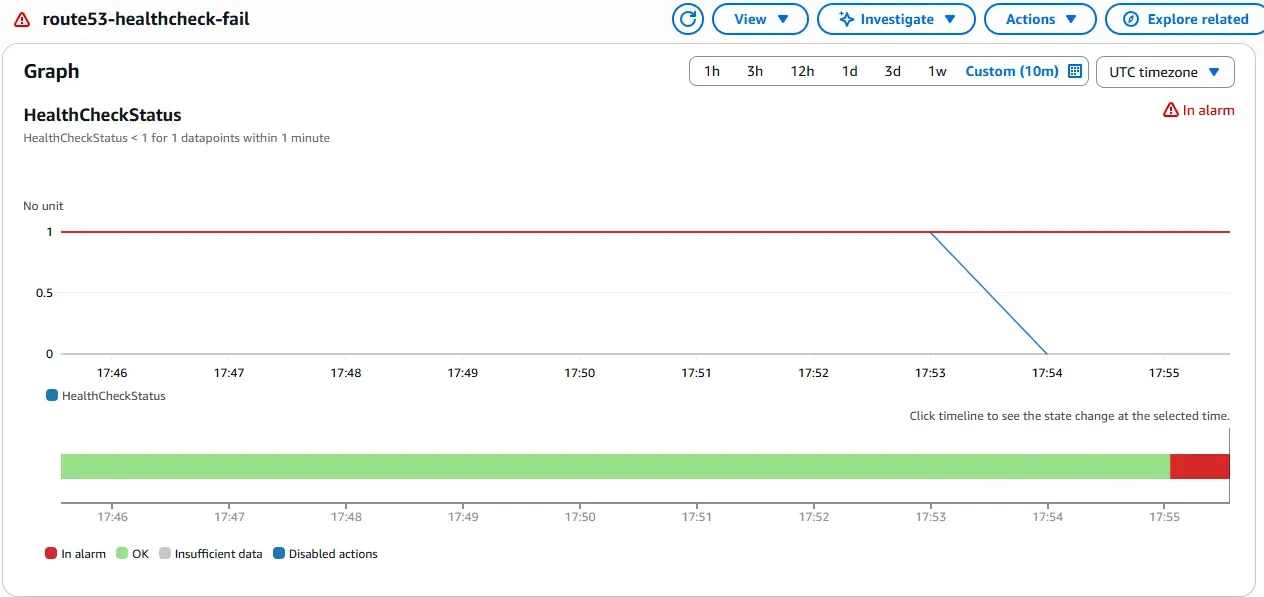
Monitoring and alerting detect primary server failures and manage recovery. Route 53 health checks probe the primary server’s public IP. When a health check fails, a CloudWatch alarm sends a notification to an SNS topic to trigger the failover process. A separate alarm detects when the server is healthy again, supporting the failback workflow.
Failover Alert (Primary Failure)
resource "aws_route53_health_check" "primary_server_check" {
type = "HTTP"
resource_path = "/"
port = 80
ip_address = module.primary_webserver.public_ip
failure_threshold = 3
request_interval = 30
}
resource "aws_cloudwatch_metric_alarm" "health_alarm" {
alarm_name = "route53-healthcheck-fail"
metric_name = "HealthCheckStatus"
namespace = "AWS/Route53"
statistic = "Minimum"
period = 60
evaluation_periods = 1
threshold = 1
comparison_operator = "LessThanThreshold"
dimensions = {
HealthCheckId = aws_route53_health_check.primary_server_check.id
}
alarm_actions = [aws_sns_topic.failover_topic.arn]
}
resource "aws_sns_topic" "failover_topic" {
name = "failover-topic"
}Failback Alert (Primary Recovery)
resource "aws_cloudwatch_metric_alarm" "failback_alarm" {
alarm_name = "route53-healthcheck-recovered"
metric_name = "HealthCheckStatus"
namespace = "AWS/Route53"
statistic = "Minimum"
period = 60
evaluation_periods = 1
threshold = 1
comparison_operator = "GreaterThanOrEqualToThreshold"
actions_enabled = false
dimensions = {
HealthCheckId = aws_route53_health_check.primary_server_check.id
}
alarm_actions = [aws_sns_topic.failback_topic.arn]
}
resource "aws_sns_topic" "failback_topic" {
name = "failback-topic"
}SSM Automation Documents
AWS Systems Manager (SSM) Automation documents define the failover and failback processes. They specify steps to start or stop the secondary instance, shift traffic with Global Accelerator, and manage CloudWatch alarms for seamless transitions without manual intervention.
IAM Role for SSM Automation
resource "aws_iam_role" "ssm_execution_role" {
name = "FailoverSSMExecutionRole"
assume_role_policy = jsonencode({
Version = "2012-10-17",
Statement = [ {
Effect = "Allow"
Principal = {
Service = "ssm.amazonaws.com"
}
Action = "sts:AssumeRole"
}
]
})
}
resource "aws_iam_role_policy" "ssm_execution_policy" {
name = "ssm-execution-permissions"
role = aws_iam_role.ssm_execution_role.id
policy = jsonencode({
Version = "2012-10-17",
Statement = [ {
Effect = "Allow"
Action = [ "ec2:StartInstances",
"ec2:DescribeInstances",
"globalaccelerator:UpdateEndpointGroup"
]
Resource = [module.secondary_webserver.instance_arn, aws_globalaccelerator_endpoint_group.primary_endpoint.arn, aws_globalaccelerator_endpoint_group.secondary_endpoint.arn]
},
{
Effect = "Allow",
Action = [ "cloudwatch:DisableAlarmActions",
"cloudwatch:EnableAlarmActions"
],
Resource = "*"
}
]
})
}run-second-instance.yaml (Starts and waits for the secondary instance)
schemaVersion: '0.3'
description: "Start and wait for the secondary instance to become healthy"
assumeRole: "{{ AutomationAssumeRole }}"
parameters:
AutomationAssumeRole:
type: String
description: "Role to assume for executing the automation"
SecondaryInstanceId:
type: String
description: "ID of the secondary EC2 instance"
mainSteps:
- name: StartSecondaryInstance
action: aws:changeInstanceState
inputs:
InstanceIds:
- "{{ SecondaryInstanceId }}"
DesiredState: running
- name: WaitForInstanceToBeHealthy
action: aws:waitForAwsResourceProperty
inputs:
Service: ec2
Api: DescribeInstanceStatus
InstanceIds:
- "{{ SecondaryInstanceId }}"
PropertySelector: "$.InstanceStatuses[0].InstanceStatus.Status"
DesiredValues:
- "ok"
MaxAttempts: 10
Interval: 15failover-doc.yaml (Shifts traffic to secondary and manages alarms)
schemaVersion: '0.3'
description: "Failover to the secondary instance and fully redirect Global Accelerator traffic"
assumeRole: "{{ AutomationAssumeRole }}"
parameters:
AutomationAssumeRole:
type: String
description: "Role to assume for executing the automation"
PrimaryInstanceId:
type: String
description: "ID of the primary EC2 instance"
PrimaryEndpointGroupArn:
type: String
description: "ARN of the Global Accelerator primary endpoint group"
SecondaryInstanceId:
type: String
description: "ID of the secondary EC2 instance"
SecondaryEndpointGroupArn:
type: String
description: "ARN of the Global Accelerator secondary endpoint group"
mainSteps:
- name: DisableFailoverAlarm
action: aws:executeAwsApi
inputs:
Service: cloudwatch
Api: DisableAlarmActions
AlarmNames:
- "route53-healthcheck-fail"
- name: EnableFailbackAlarm
action: aws:executeAwsApi
inputs:
Service: cloudwatch
Api: EnableAlarmActions
AlarmNames:
- "route53-healthcheck-recovered"
- name: ShiftTrafficToSecondary
action: aws:executeAwsApi
inputs:
Service: GlobalAccelerator
Api: UpdateEndpointGroup
EndpointGroupArn: "{{ SecondaryEndpointGroupArn }}"
EndpointConfigurations:
- EndpointId: "{{ SecondaryInstanceId }}"
Weight: 100
- name: RemoveTrafficFromPrimary
action: aws:executeAwsApi
inputs:
Service: GlobalAccelerator
Api: UpdateEndpointGroup
EndpointGroupArn: "{{ PrimaryEndpointGroupArn }}"
EndpointConfigurations:
- EndpointId: "{{ PrimaryInstanceId }}"
Weight: 0shut-second-instance.yaml (Stops the secondary instance)
schemaVersion: "0.3"
description: "Shutdown the secondary EC2 instance"
assumeRole: "{{ AutomationAssumeRole }}"
parameters:
AutomationAssumeRole:
type: String
description: "Role to assume for executing the automation"
SecondaryInstanceId:
type: String
description: "ID of the secondary EC2 instance"
mainSteps:
- name: StopSecondaryInstance
action: aws:changeInstanceState
inputs:
InstanceIds:
- "{{ SecondaryInstanceId }}"
DesiredState: stoppedLambda Functions
Two Lambda functions handle automated failover and failback. Triggered by SNS notifications from CloudWatch alarms, they invoke SSM Automation documents to start or stop EC2 instances and update Global Accelerator routing.
IAM Role and Policy
resource "aws_iam_role" "iam_for_lambda" {
name = "lambda_iam_for_ssm_2"
assume_role_policy = data.aws_iam_policy_document.lambda_assume_role.json
}
resource "aws_iam_role_policy" "iam_lambda_policy" {
name = "failover_policy"
role = aws_iam_role.iam_for_lambda.id
policy = jsonencode({
Version = "2012-10-17",
Statement = [ {
Effect = "Allow",
Action = ["ssm:StartAutomationExecution","ssm:GetAutomationExecution"],
Resource = [ "${aws_ssm_document.failover_doc.arn}:$LATEST",
"${aws_ssm_document.failback_doc.arn}:$LATEST",
"${aws_ssm_document.shutdown_second_instance.arn}:$LATEST",
"${aws_ssm_document.run_second_instance.arn}:$LATEST"
]
},
{
Effect = "Allow",
Action = "iam:PassRole",
Resource = aws_iam_role.ssm_execution_role.arn
},
{
Effect = "Allow",
Action = ["logs:CreateLogGroup","logs:CreateLogStream","logs:PutLogEvents"],
Resource = "*"
}
]
})
}Failover Lambda Function
resource "aws_lambda_function" "failover_handler" {
filename = data.archive_file.failover_archive.output_path
function_name = "failover-lambda"
handler = "function.handler"
runtime = "nodejs20.x"
role = aws_iam_role.iam_for_lambda.arn
source_code_hash = data.archive_file.failover_archive.output_base64sha256
environment {
variables = {
AUTOMATION_DOCUMENT_NAME = aws_ssm_document.failover_doc.name
RUN_SECOND_INSTANCE_DOCUMENT_NAME = aws_ssm_document.run_second_instance.name
AUTOMATION_ASSUME_ROLE_ARN = aws_iam_role.ssm_execution_role.arn
PRIMARY_INSTANCE_ID = module.primary_webserver.ec2_id
PRIMARY_ENDPOINT_GROUP_ARN = aws_globalaccelerator_endpoint_group.primary_endpoint.arn
SECONDARY_INSTANCE_ID = module.secondary_webserver.ec2_id
SECONDARY_ENDPOINT_GROUP_ARN = aws_globalaccelerator_endpoint_group.secondary_endpoint.arn
}
}
}
resource "aws_sns_topic_subscription" "failover_sub" {
topic_arn = aws_sns_topic.failover_topic.arn
protocol = "lambda"
endpoint = aws_lambda_function.failover_handler.arn
}
resource "aws_lambda_permission" "allow_sns_failover" {
statement_id = "AllowExecutionFromSNS"
action = "lambda:InvokeFunction"
function_name = aws_lambda_function.failover_handler.function_name
principal = "sns.amazonaws.com"
source_arn = aws_sns_topic.failover_topic.arn
}Failback Lambda Function
resource "aws_lambda_function" "failback_handler" {
filename = data.archive_file.failback_archive.output_path
function_name = "failback-lambda"
handler = "function.handler"
runtime = "nodejs20.x"
role = aws_iam_role.iam_for_lambda.arn
source_code_hash = data.archive_file.failback_archive.output_base64sha256
environment {
variables = {
AUTOMATION_DOCUMENT_NAME = aws_ssm_document.failback_doc.name
SHUTDOWN_SECOND_INSTANCE_DOCUMENT_NAME = aws_ssm_document.shutdown_second_instance.name
AUTOMATION_ASSUME_ROLE_ARN = aws_iam_role.ssm_execution_role.arn
PRIMARY_INSTANCE_ID = module.primary_webserver.ec2_id
PRIMARY_ENDPOINT_GROUP_ARN = aws_globalaccelerator_endpoint_group.primary_endpoint.arn
SECONDARY_INSTANCE_ID = module.secondary_webserver.ec2_id
SECONDARY_ENDPOINT_GROUP_ARN = aws_globalaccelerator_endpoint_group.secondary_endpoint.arn
}
}
}
resource "aws_sns_topic_subscription" "failback_sub" {
topic_arn = aws_sns_topic.failback_topic.arn
protocol = "lambda"
endpoint = aws_lambda_function.failback_handler.arn
}
resource "aws_lambda_permission" "allow_sns_failback" {
statement_id = "AllowExecutionFromSNSFailback"
action = "lambda:InvokeFunction"
function_name = aws_lambda_function.failback_handler.function_name
principal = "sns.amazonaws.com"
source_arn = aws_sns_topic.failback_topic.arn
}Tests & Validation
Normal Operating State
The system runs in its default, steady state with traffic served from the primary region in Paris. The primary EC2 instance is powered on and healthy. Route 53 health checks confirm availability, CloudWatch alarms remain in the OK state, and Global Accelerator routes all traffic to the primary endpoint with static IP continuity.
EC2 Instance Running (Paris Region)

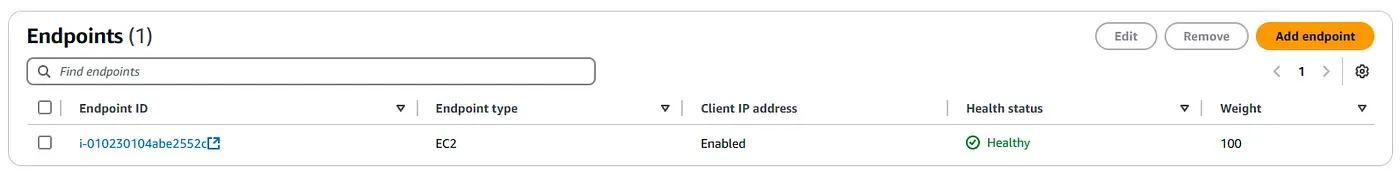
Global Accelerator Endpoint Configuration
Browser Rendering Through Accelerator IP

Route 53 Health Check Status

CloudWatch Alarm in OK State
Failover State (Secondary Region Active)
When the primary server in Paris is unavailable, traffic is automatically redirected to the secondary server in London. The Route 53 health check detects the failure and triggers a CloudWatch alarm, which invokes a Lambda function to start the standby instance and update Global Accelerator routing. The transition is seamless for users, maintaining access via the same static IP.
CloudWatch Alarm
EC2 Instance in London

User-Facing Result via Global Accelerator IP
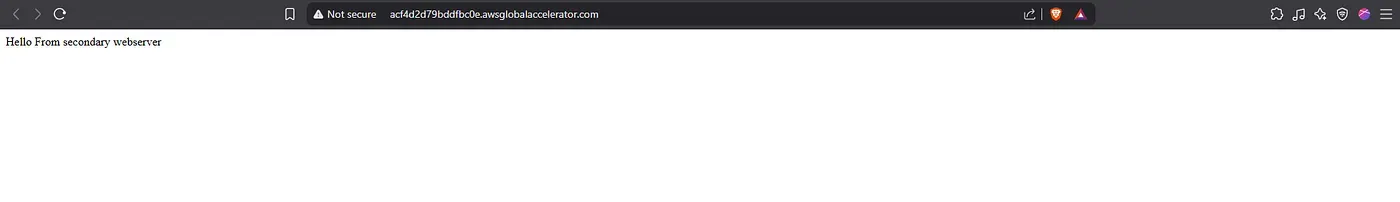
The same workflow also handles the reverse scenario automatically. When the primary server becomes healthy again, routing is restored to Paris without manual intervention.
Conclusion
By integrating Terraform with AWS Global Accelerator, Route 53, CloudWatch, Lambda, and Systems Manager, this architecture delivers a fully automated regional disaster recovery solution. It ensures sustained service availability without operator involvement, while maintaining a secure, modular, and compliant infrastructure aligned with best practices in fault tolerance.