Securing a Serverless AWS Infrastructure with Terraform

This is a personal project. Full implementation available on GitHub
SwiftSupport is an AI-powered support ticket platform that recently transitioned to a modern serverless architecture on AWS. While the initial deployment focused on rapid functionality, security best practices were not prioritized. With the platform now servicing multiple clients and sensitive customer interactions, it became crucial to overhaul access control, implement fine-grained IAM policies, and enforce a secure infrastructure as code approach. The goal was to strengthen the AWS environment, redesign identity and access structures, and enforce the principle of least privilege, all while maintaining automation and scalability with Terraform.
Table of Contents
Implementation Strategy
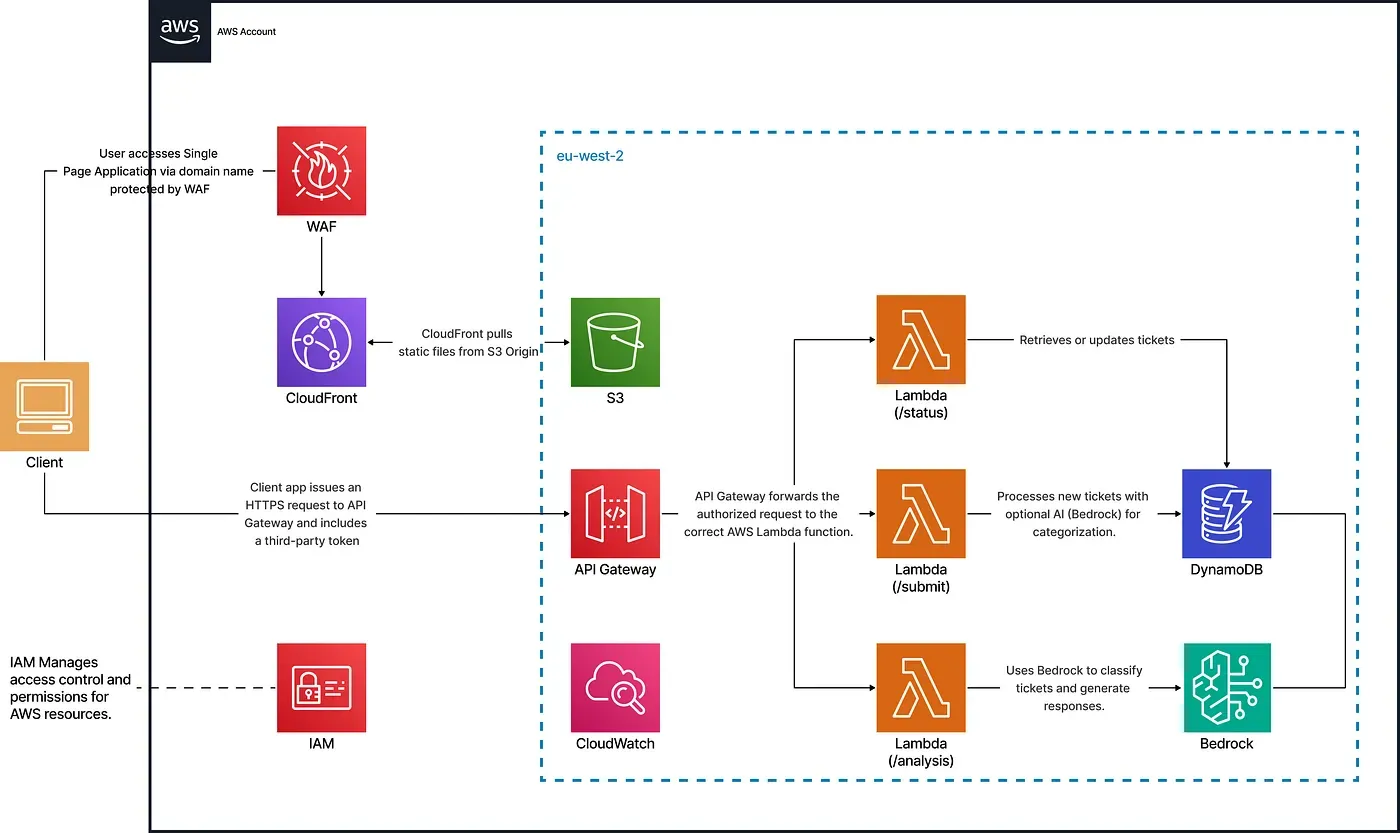
This solution replaces shared AWS credentials with IAM Identity Center for single sign-on, enforces role-based access control with IAM groups and policies, and applies the principle of least privilege through scoped permissions and permission boundaries. It uses a modular, secure-by-default Terraform setup to harden key AWS services, including Lambda, API Gateway, and CloudFront, while automating infrastructure provisioning and managing SSO-based access to monitoring and cost tools.
Technical Implementation
IAM Identity Center & Groups
To eliminate shared credentials and enforce role-based access control, IAM Identity Center was configured with five dedicated groups for Developers, DevOps, Security, Data Science, and Product Management. Each group maps to specific roles and inline policies defining least-privilege access.
module "iam_identity_center" {
source = "./modules/security/iam-identity-center"
groups = local.groups
}Each group is defined in the locals block with custom users and permissions:
locals {
groups = {
Developers = {
description = "Developer team"
users = [ {
user_name = "dev01"
given_name = "Dev"
family_name = "One"
email = "dev01@example.com"
}
# ... other developers here
]
permissions = [ {
actions = [ "lambda:InvokeFunction",
"lambda:UpdateFunctionCode",
"lambda:GetFunction",
"lambda:ListFunctions",
"lambda:GetFunctionConfiguration"
]
resources = [for name, mod in module.lambda : mod.arn]
}
# ... more permissions here
]
}
# other groups...
}
}IAM Permission Boundaries
By enforcing permission boundaries, all role permissions remain tightly scoped, reducing the risk of misconfiguration and ensuring consistent security governance. A customer-managed boundary policy was created and applied to high-privilege roles such as DevOps to prevent potential privilege escalation.
resource "aws_iam_policy" "permission_boundary" {
name = "devops-boundary"
policy = file("${path.module}/boundary.json")
}Then attached it to DevOps roles:
resource "aws_ssoadmin_permissions_boundary_attachment" "devops_boundary" {
for_each = {
for group_name, group in var.groups :
group_name => group.permission_boundaries
if contains(keys(group), "permission_boundaries") && group.permission_boundaries != null
}
instance_arn = tolist(data.aws_ssoadmin_instances.main.arns)[0]
permission_set_arn = aws_ssoadmin_permission_set.this[each.key].arn
permissions_boundary {
customer_managed_policy_reference {
name = each.value
path = "/"
}
}
}Lambda Security and Modularization
Each Lambda function is provisioned with a dedicated IAM role and scoped permissions defined in the locals block. This modular approach reduces policy duplication, ensures consistent security, and simplifies ongoing maintenance.
Locals block defining Lambda configurations
locals {
lambdas = {
status = {
name = "status"
source_dir = "./lambdas/status"
output_path = "./lambdas/status.zip"
env_vars = {}
policy = jsonencode({
Version = "2012-10-17",
Statement = [ {
Effect = "Allow",
Action = [ "dynamodb:GetItem",
"dynamodb:PutItem",
"dynamodb:UpdateItem",
"dynamodb:Query"
],
Resource = module.dynamodb.arn
},
{
Effect = "Allow",
Action = [ "logs:CreateLogGroup",
"logs:CreateLogStream",
"logs:PutLogEvents"
],
Resource = "arn:aws:logs:*:*:*"
}
]
})
}
# ... other Lambda configurations (submit, analysis, etc.)
}
}Lambda Module Definition This module provisions the IAM role, policy, and Lambda function for each defined configuration.
resource "aws_iam_role" "iam_for_lambda" {
name = "${var.lambda_config.name}_role"
assume_role_policy = var.assume_role_policy
}
resource "aws_iam_role_policy" "iam_lambda_policy" {
name = "${var.lambda_config.name}_policy"
role = aws_iam_role.iam_for_lambda.name
policy = var.lambda_config.policy
}
data "archive_file" "lambda_zip" {
type = "zip"
source_dir = var.lambda_config.source_dir
output_path = var.lambda_config.output_path
}
resource "aws_lambda_function" "lambda_function" {
filename = var.lambda_config.output_path
function_name = var.lambda_config.name
role = aws_iam_role.iam_for_lambda.arn
handler = "function.handler"
runtime = "nodejs20.x"
source_code_hash = data.archive_file.lambda_zip.output_base64sha256
environment {
variables = var.lambda_config.env_vars
}
}Usage of the Lambda Module The module is invoked in the root configuration to provision all defined Lambda functions dynamically:
module "lambda" {
for_each = local.lambdas
source = "./modules/infra/lambda"
lambda_config = each.value
}API Gateway with JWT Authorization
JWT-based authorization was implemented to ensure that only authenticated users can access the Lambda-powered API endpoints. This approach improves security by validating user identity before any request is processed.
resource "aws_apigatewayv2_authorizer" "jwt" {
api_id = aws_apigatewayv2_api.api.id
name = "JWTAuthorizer"
authorizer_type = "JWT"
identity_sources = ["$request.header.Authorization"]
jwt_configuration {
issuer = "https://dev-abc123.us.auth0.com/"
audience = ["https://api.swift-support.com"]
}
}CloudFront + S3 Hardening
To prevent public access to sensitive static content, S3 buckets were secured with encryption, public access was blocked, and access was limited exclusively to CloudFront for secure CDN delivery.
resource "aws_s3_bucket" "s3_bucket" {}
resource "aws_s3_bucket_server_side_encryption_configuration" "s3_encryption" {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.s3_bucket.id
rule {
apply_server_side_encryption_by_default {
sse_algorithm = "AES256"
}
}
}
resource "aws_s3_bucket_public_access_block" "website_public_access" {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.s3_bucket.id
block_public_acls = true
block_public_policy = true
ignore_public_acls = true
restrict_public_buckets = true
}
resource "aws_s3_bucket_policy" "cloudfront_access" {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.s3_bucket.id
policy = jsonencode({
Version = "2012-10-17",
Statement = [ {
Sid = "AllowCloudFrontService"
Effect = "Allow"
Principal = {
Service = "cloudfront.amazonaws.com"
}
Action = ["s3:GetObject"]
Resource = "${aws_s3_bucket.s3_bucket.arn}/*"
Condition = {
StringEquals = {
"AWS:SourceArn" = var.cloudfront_distribution_arn
}
}
}
]
})
}WAF & CloudTrail
AWS WAF was configured with managed rule groups to protect the CloudFront distribution from common web threats such as SQL injection and malicious inputs. CloudWatch metrics were enabled for visibility into blocked requests.
resource "aws_wafv2_web_acl" "cloudfront_waf" {
name = "cloudfront-waf"
scope = "CLOUDFRONT"
rule {
name = "AWSManagedRulesSQLiRuleSet"
priority = 2
override_action { none {} }
statement {
managed_rule_group_statement {
name = "AWSManagedRulesSQLiRuleSet"
vendor_name = "AWS"
}
}
visibility_config {
cloudwatch_metrics_enabled = true
metric_name = "SQLiRuleSet"
sampled_requests_enabled = true
}
}
}CloudTrail was enabled to capture all API activity across the account for auditing and compliance.
resource "aws_s3_bucket" "cloudtrail_bucket" {}
resource "aws_s3_bucket_ownership_controls" "cloudtrail_controls" {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.cloudtrail_bucket.id
rule {
object_ownership = "BucketOwnerPreferred"
}
}
resource "aws_s3_bucket_acl" "cloudtrail_acl" {
depends_on = [aws_s3_bucket_ownership_controls.cloudtrail_controls]
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.cloudtrail_bucket.id
acl = "private"
}
resource "aws_s3_bucket_policy" "cloudtrail_policy" {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.cloudtrail_bucket.id
policy = jsonencode({
Version = "2012-10-17",
Statement = [ {
Sid : "AWSCloudTrailAclCheck",
Effect : "Allow",
Principal = {
Service = "cloudtrail.amazonaws.com"
},
Action = "s3:GetBucketAcl",
Resource = aws_s3_bucket.cloudtrail_bucket.arn
},
{
Sid = "AWSCloudTrailWrite"
Effect = "Allow"
Principal = { Service = "cloudtrail.amazonaws.com" }
Action = "s3:PutObject"
Resource = "${aws_s3_bucket.cloudtrail_bucket.arn}/AWSLogs/${data.aws_caller_identity.current.account_id}/*"
Condition = {
StringEquals = {
"s3:x-amz-acl" : "bucket-owner-full-control"
}
}
}
]
})
}
resource "aws_cloudtrail" "main" {
name = "main-trail"
s3_bucket_name = aws_s3_bucket.cloudtrail_bucket.bucket
include_global_service_events = true
is_multi_region_trail = true
enable_log_file_validation = true
}Conclusion
This project transforms the infrastructure from a functionality-focused model to a secure, scalable, and governed environment. Using Terraform, the implementation delivers fine-grained IAM with Identity Center, secure Lambda and API Gateway integrations, and hardened S3, WAF, and CloudFront configurations. Access is now auditable and role-based, supporting best practices in cloud governance while enabling confident scaling.